Shoulder replacement surgery involves replacing damaged parts of the shoulder joint with artificial components with the goal of relieving pain and improving mobility. In this post, we’ll explore what the procedure entails, who might be a candidate for it, and what recovery typically looks like.
Key Takeaways
- In shoulder replacement surgery, the damaged parts of the shoulder joint are replaced with artificial components.
- Common conditions treated with shoulder replacement include arthritis, shoulder fractures, rotator cuff tear arthropathy, and osteonecrosis.
- Recovery often requires careful pre-surgery preparation and a structured physical therapy plan post-surgery to restore strength and mobility.
Understanding Shoulder Replacement Surgery
Shoulder replacement surgery, also known as shoulder arthroplasty, is a procedure in which damaged parts of the shoulder joint are replaced with artificial components. The primary goal of shoulder replacement surgery is to relieve pain and improve mobility, allowing patients to resume their daily activities with less discomfort.
There are different types of shoulder replacement surgeries tailored to various conditions and needs:
- Total shoulder replacement involves replacing both the ball (humeral head) and the socket (glenoid bone) of the shoulder joint.
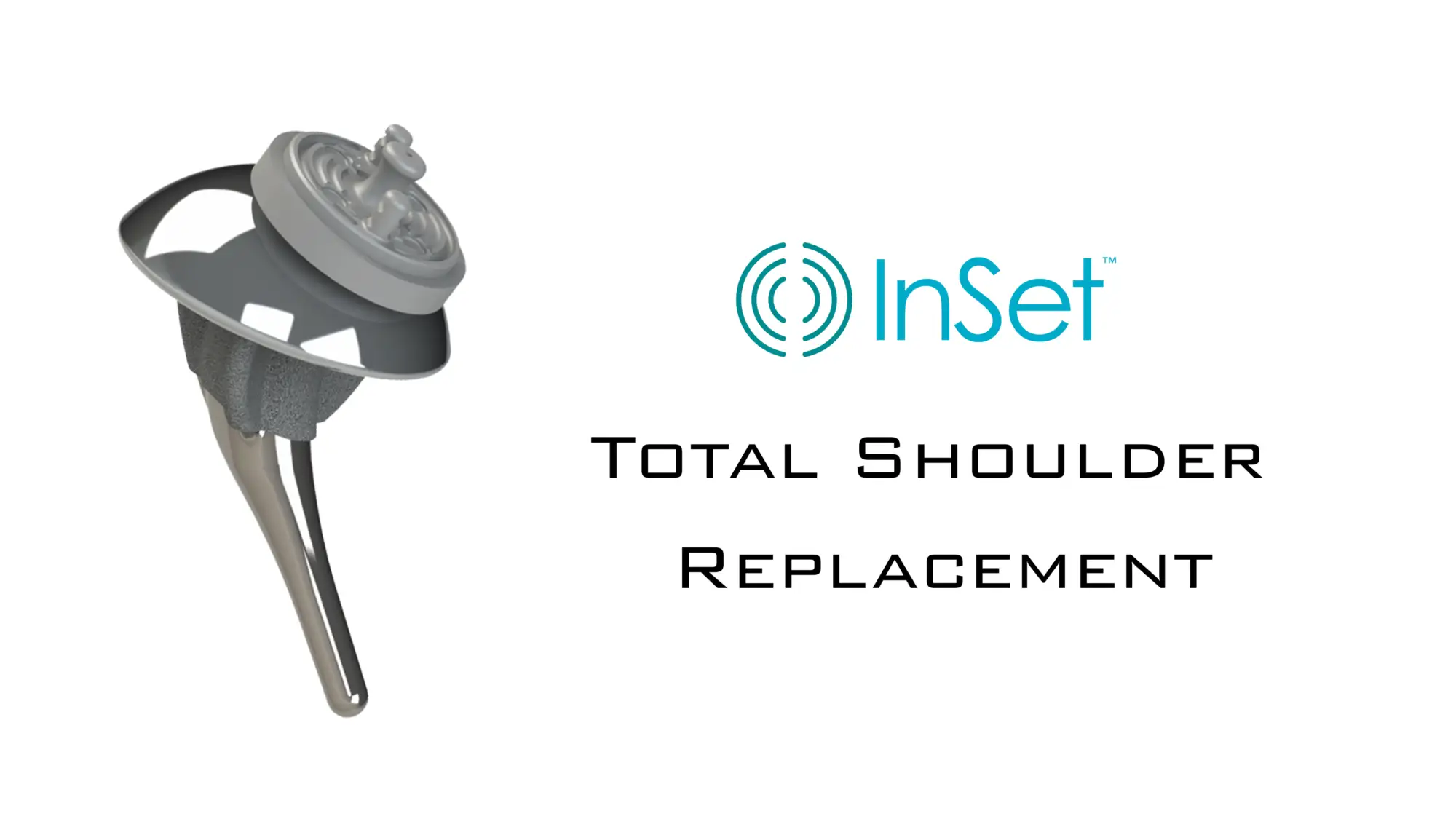
- Reverse shoulder replacement is where the ball and socket positions are reversed. In many cases, this design may be more effective for patients with severe rotator cuff damage.

The aim is not only to relieve severe shoulder pain and improve shoulder motion, but also to enhance the overall quality of life for the patients.
Conditions Treated by Shoulder Replacement
Shoulder replacement surgery may be a treatment option for various painful conditions that affect the shoulder joint. One of the most common reasons for this surgery is shoulder arthritis, which includes osteoarthritis, inflammatory arthritis, and post-traumatic arthritis. These conditions can cause cartilage breakdown, resulting in pain and stiffness.
In addition to arthritis, severe shoulder fractures, particularly in older individuals, can necessitate shoulder replacement surgery. If the fracture cannot be repaired by other methods, joint replacement surgery may become an appropriate option to restore function and alleviate pain.
Rotator cuff tear arthropathy is another condition that may require shoulder replacement. This typically occurs when a rotator cuff tear leads to joint destruction, resulting in severe shoulder pain and impaired mobility. Osteonecrosis, a condition where blood flow to the shoulder bone is disrupted, causing the bone to collapse, may also be treated with shoulder replacement surgery.
Each of these conditions can significantly affect daily life, and shoulder replacement may be considered when pain and loss of mobility become severe.
Who Should Consider Shoulder Replacement?
Candidates for shoulder replacement are typically those who experience persistent pain, stiffness, and limitations in daily activities despite non-surgical treatments.
Age is not the sole determining factor for undergoing shoulder replacement surgery. Both younger and older patients can be good candidates, depending on the severity of their condition and overall health. However, certain health conditions may disqualify someone from being a candidate for the procedure.
Shoulder replacement surgery is a decision that requires careful consideration of the potential benefits and risks. An experienced shoulder specialist[TM2] can evaluate the condition and help guide the most appropriate treatment path. Together, you can decide on the best course of action.
Pre-Surgery Preparations
Ahead of the procedure, you will receive specific instructions from your surgeon’s team. However, before the procedure, the following steps will likely be necessary:
- A thorough evaluation of medical history, medications, and lifestyle habits.
- A complete physical examination to assess readiness for surgery.
- Identification of any potential risks through pre-operative testing.
A few days before the surgery, you may be advised to stop taking blood thinners and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Planning for the recovery period is also important. In many cases, patients arrange for someone to assist with daily tasks during the initial recovery period. Preparing meals in advance can help ease the burden during the early stages of recovery.
The Surgical Procedure
Typically, the surgery lasts from 1 to 2 hours, though the duration may vary depending on individual circumstances. Patients are placed under anesthesia, which is discussed ahead of the procedure.
During the procedure, the surgeon will remove the damaged parts of the shoulder joint and replace them with a metal ball and a plastic socket. After the surgery, the patient is monitored in a recovery area.
Depending on your overall health and the specifics of the surgery, you may either be discharged home the same day or stay overnight for further observation. The goal is to manage any immediate post-surgery issues and ensure that you are stable and comfortable before going home to begin the recovery process.
Recovery Timeline
After the surgery, your arm will likely be immobilized in a removable sling for a couple of weeks to protect the site and prevent unnecessary movement. Your doctor will recommend medications to help manage pain.
Physical therapy typically begins shortly post-surgery. Many patients can perform light activities within a few weeks, but full recovery may take several months. Throughout the recovery period, it’s important to follow your surgeon’s and physical therapist’s instructions and rehabilitation guidance.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Physical therapy is an important part of the recovery process after shoulder replacement surgery. Your physical therapist will work with you to learn safe movement techniques and exercises designed for recovery.
Strengthening exercises and functional training are integral parts of the rehabilitation process. These exercises help restore function and smooth movement of the shoulder joint. Your physical therapist will tailor an exercise program specific to your needs, helping to reduce pain and improve mobility.
For many patients, a structured rehabilitation plan may improve long-term results and help with returning to normal activities more comfortably.
Summary
In conclusion, shoulder replacement surgery may be an option for those suffering from severe shoulder pain and impaired mobility due to various conditions. By understanding the procedure, preparing adequately, and committing to a thorough recovery plan, many patients report improvements in their quality of life. If you’re considering shoulder replacement surgery, consult with a shoulder specialist to discuss your options.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the benefits of total shoulder replacement surgery?
For many patients, total shoulder replacement surgery has been shown to help relieve pain, enhance shoulder mobility, and facilitate a return to everyday activities and an active lifestyle.
What bones make up the shoulder joint?
The shoulder joint is formed by three key bones: the humerus, scapula, and clavicle.
What condition is commonly treated with total shoulder replacement surgery?
Total shoulder replacement surgery is commonly used to treat shoulder arthritis, alleviating pain and restoring mobility. However, many other conditions may also warrant total shoulder replacement surgery.
How is shoulder arthritis initially treated?
Shoulder arthritis is generally initially treated with nonsurgical methods such as physical therapy and reducing activity levels to manage pain and improve function. If nonsurgical treatments fail to provide adequate relief, surgery may be recommended.